Create a Calculator Mobile App with MIT App Inventor
Tutorial plan
1- Objective of calculator Mobile App
2- Description of application designer interface
3- Description of application blocks part
Objective of calculator Mobile App
The objective of the Calculator Mobile App is to provide users with a simple and efficient tool to perform basic mathematical calculations directly on their mobile devices. Developed using MIT App Inventor, the app allows users to carry out arithmetic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division in a user-friendly interface.
It is designed to be intuitive, enabling users to input numbers and operators easily and receive instant results. Beyond its practical functionality, the app also serves an educational purpose, demonstrating the principles of mobile app development, event-driven programming, and user interface design in MIT App Inventor.
Ultimately, the app aims to combine convenience, accessibility, and learning, making it a practical tool for everyday calculations as well as a project to develop programming skills.
Description of application designer interface
The designer interface is where you arrange and style the labels (for displaying results), buttons (for input), and arrangements (for structure). Each component plays a specific role to make the calculator functional and user-friendly.
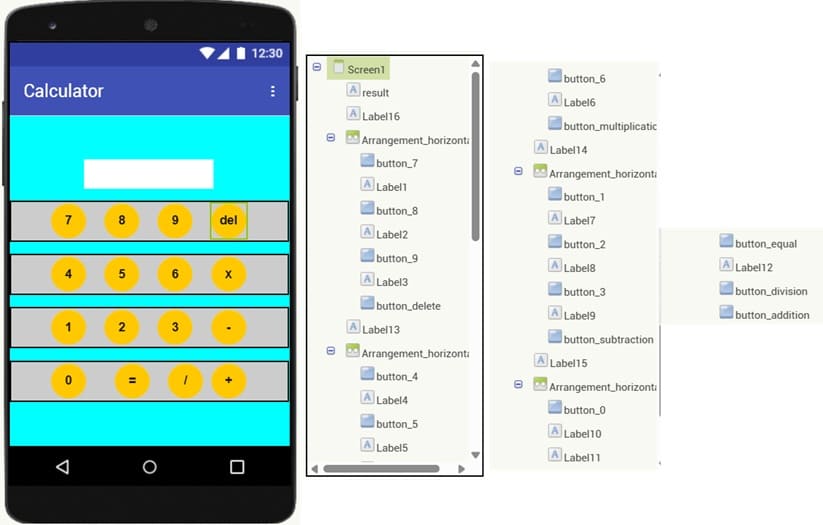
1. Screen (Screen1)
Role: Main container of the application.
It holds all the visual components (buttons, labels, arrangements).
2. Horizontal Arrangements
Role: Organize the layout of the app.
HorizontalArrangement: Puts buttons side by side (ex: 7 8 9 ÷).
This ensures the calculator looks like a real keypad.
3. Label Result
Role: Shows the numbers entered and the final result of calculations.
Example: when user presses 7 + 3, the label updates to show 10.
4. Buttons (0–9)
Role: Allow user to input digits.
Each button appends its number to the current operation string.
5. Buttons for Operators (+, −, ×, ÷)
Role: Allow user to select the mathematical operation.
When clicked, they store the operator and prepare for the next number.
6. Equal Button (=)
Role: Executes the chosen operation.
Uses the stored values (number1, number2, operator) to compute the result and display it in the label.
7. Delete Button
Role: Removes the last digit or operator typed.
Useful for correcting mistakes without resetting everything.
Description of application blocks part
The role of the Blocks part is to make the Calculator app interactive and functional.
It connects user actions (button clicks) to the app’s logic (calculations).
It ensures that inputs are stored, processed, and displayed correctly.
Without the Blocks part, the calculator would only be a static design with no functionality.
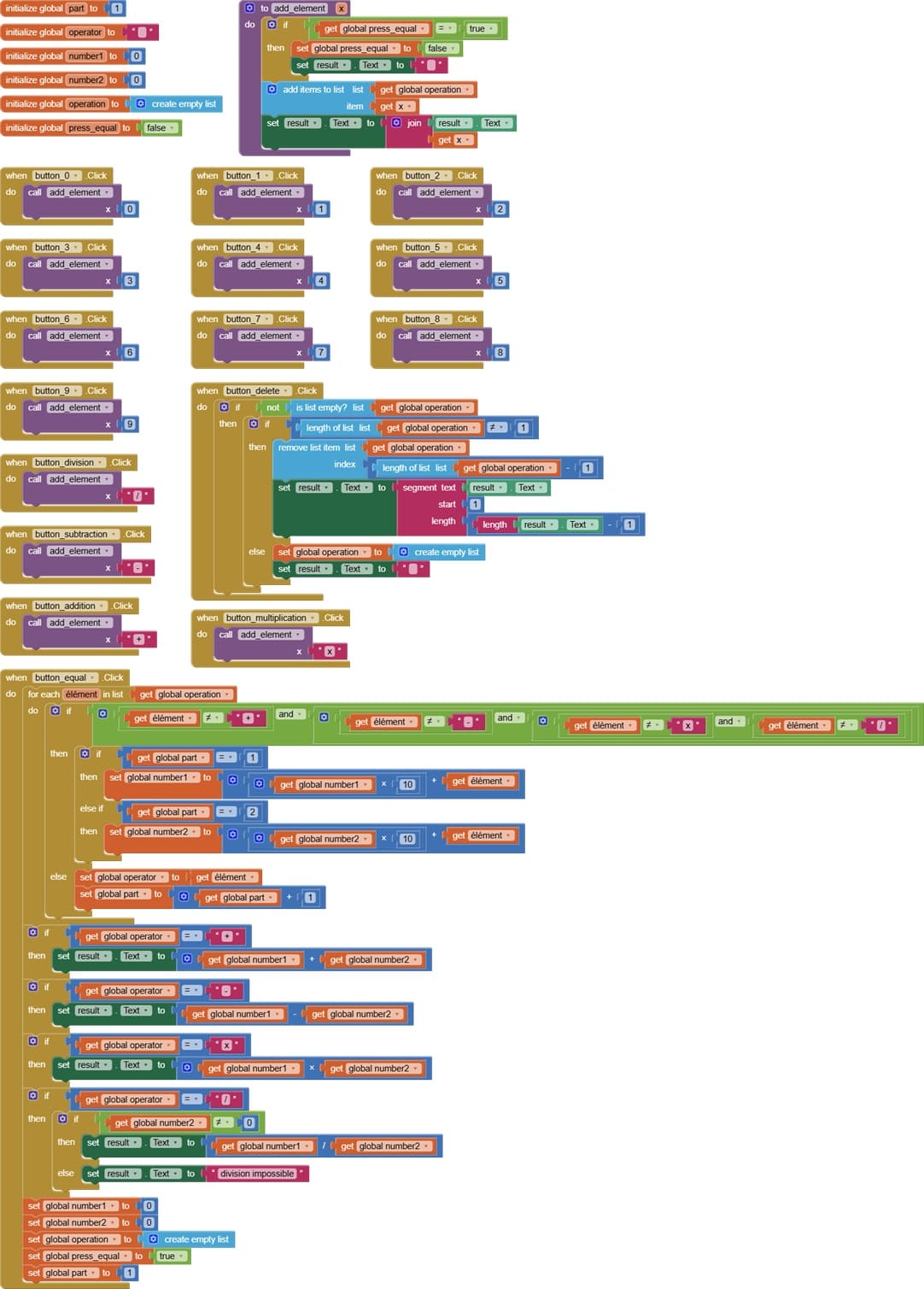
1. initialization of variables

Create the Calculator Variables :
partie → to know which part of the operation the user is typing (number1 or number2).
operateur → to store the chosen operation (+, -, ×, /).
nombre1 → to store the first number.
nombre2 → to store the second number.
operation → to store the whole expression as text (for display).
appui_egal → to check if the equal button has been pressed.
The role of variables initialization is to set default values at the beginning of the program so that the calculator starts in a stable state, avoids errors, and is ready to correctly process user inputs and operations.
2. add_element procedure
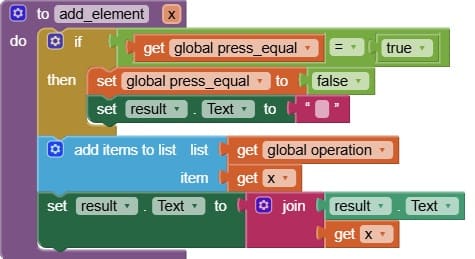
The add_element procedure is used whenever the user presses a button (digit, operator, or decimal point).
The procedure adds the pressed button’s value (element) to the current operation (a text string or a list of elements).
It ensures that the operation is displayed correctly on the result label or screen.
3. when button_number.Click
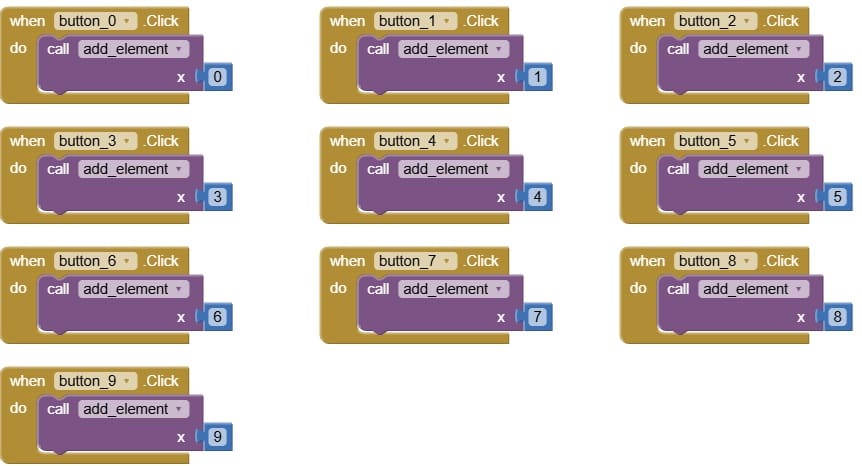
when Button_number.Click detects the user’s action when they press a number button (0–9).
Inside this event, you don’t directly write all the logic. Instead, you usually call the procedure add_element and pass the number value as a parameter.
4. when button_delete.Click
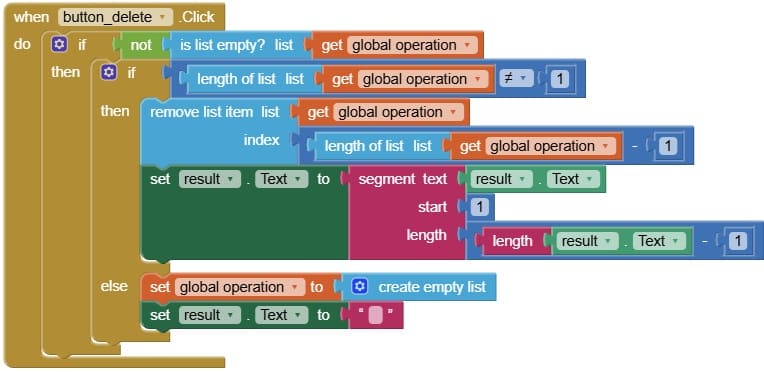
when Button_delete.Click detects when the user clicks the delete button.
Its job is to remove the last entered element (a digit, operator, or decimal point) from the current expression.
After deleting, it updates the display label so the user sees the corrected expression.
5. when button_operator.Click
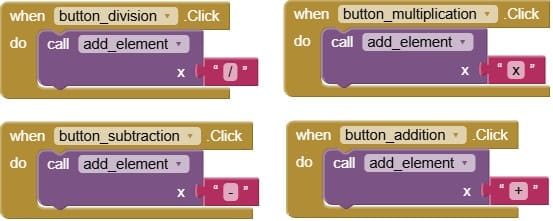
when Button_operator.Click detects when the user presses an operator button (like +, -, ×, or ÷).
Typically, it calls a procedure (often add_element or a similar one) and passes the operator as a parameter.
It adds the operator to the current mathematical expression, just like number buttons add digits.
6. when button_equal.Click
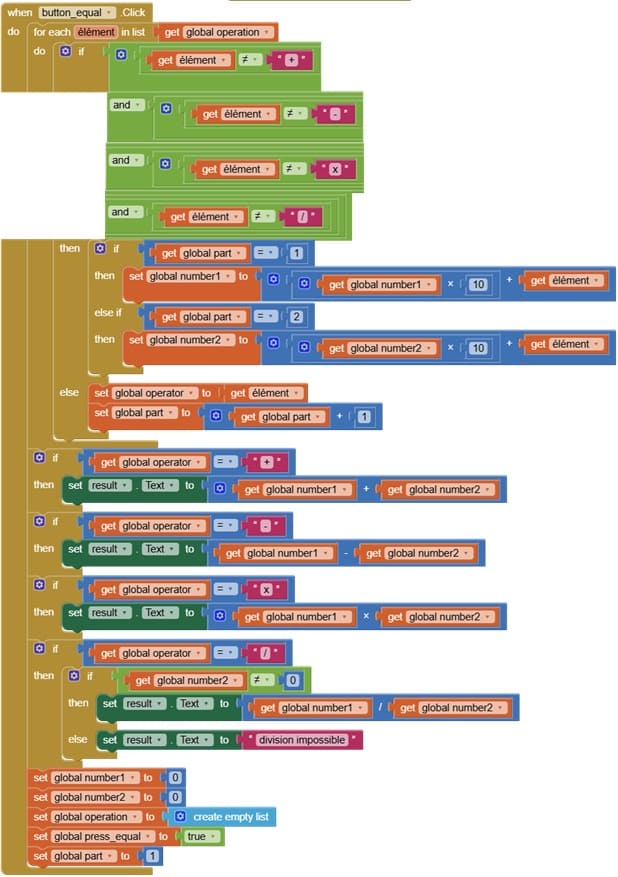
when Button_equal.Click detects when the user presses the “=” button.
Its main job is to calculate the result of the current mathematical expression that the user has built using numbers and operators.
Usually, it calls a procedure that:
Reads the stored expression (often a list or a text string).
Processes it step by step to perform the arithmetic operations.
Generates the final result.
It updates the display label to show the result of the calculation.
After execution, it may reset or clear some variables so the user can start a new calculation.
























