Measuring Distance Using HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor and ESP8266 NodeMCU
Tutorial plan
1- Objective of the tutorial
2- Working principle of the HC-SR04 sensor
3- The necessary components
4- ESP8266 Assembly with I2C LCD Display and HC-SR04 sensor
5- Program ESP8266 NodeMCU with MicroPython
Objective of the tutorial
The objective of this tutorial is to measure the distance between an object and the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor, and to display the measured value using the ESP8266 NodeMCU microcontroller.
This project aims to teach how to use the HC-SR04 sensor to detect objects and calculate distances by measuring the time taken for ultrasonic waves to travel to the object and back.
The ESP8266 NodeMCU will be programmed to send the trigger signal, read the echo response, compute the distance, and display it (for example, on the serial monitor or an LCD screen).
Through this tutorial, you will learn to:
- understand the working principle of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor.
- interface the sensor with the ESP8266 NodeMCU.
- write a MicroPython program to calculate and display the distance.
- apply this concept to real-world applications, such as obstacle detection, smart parking systems, and distance-based automation projects.
Working principle of the HC-SR04 sensor

The HC-SR04 is an ultrasonic distance measurement sensor that determines the distance between the sensor and an object without physical contact. It operates using the principle of ultrasonic sound reflection, similar to how bats and dolphins navigate and detect objects.
1. Main Components
The HC-SR04 module consists of:
- Ultrasonic Transmitter (Trigger): Emits high-frequency sound waves (around 40 kHz).
- Ultrasonic Receiver (Echo): Detects the sound waves reflected back from an object.
- Control Circuit: Measures the time taken for the sound waves to return after reflection.
2. How It Works
1- The ESP8266 NodeMCU sends a trigger pulse of about 10 microseconds to the sensor’s Trigger pin.
2- Upon receiving this pulse, the sensor emits 8 cycles of ultrasonic waves at 40 kHz through the transmitter.
3- These waves travel through the air and, when they hit an obstacle, they bounce back toward the sensor.
4- The Echo pin of the sensor goes HIGH for the duration that corresponds to the time taken by the sound wave to travel to the object and back.
5- The microcontroller measures this time interval and uses it to calculate the distance.
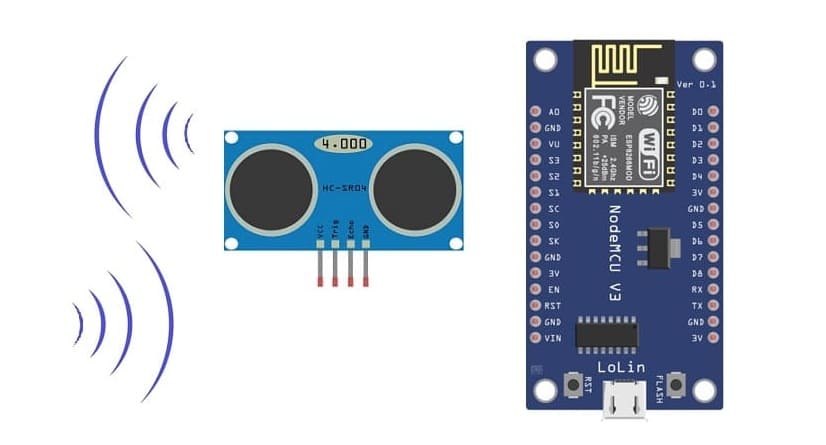
The necessary components
1. ESP8266 NodeMCU Board

The NodeMCU is a microcontroller board based on the ESP8266 Wi-Fi module.
It allows you to write and upload programs using MicroPython or the Arduino IDE.
In this project, it serves as the main controller that:
a) Sends the Trigger signal to the ultrasonic sensor.
b) Reads the Echo signal and calculates the distance.
c) Sends the measured distance to the LCD I2C display.
2. HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor

This sensor measures the distance to an obstacle using ultrasonic waves.
It consists of two transducers:
a) A transmitter, which emits sound waves at 40 kHz.
b) A receiver, which detects the reflected waves.
The sensor calculates the time difference between sending and receiving the waves to determine the distance.
3. LCD I2C Display (20x4)
The LCD 16x2 (20 characters × 4 lines) is used to display the measured distance in centimeters.
4. Breadboard

The breadboard allows you to build the circuit easily without soldering.
It’s used to connect all components together in a clean and organized way.
5. Jumper Wires

A set of male-to-male and male-to-female jumper wires will be used to make the connections between:
a) The ESP8266 NodeMCU and the HC-SR04 sensor
b) The ESP8266 NodeMCU and the LCD I2C display
ESP8266 Assembly with I2C LCD Display and HC-SR04 sensor
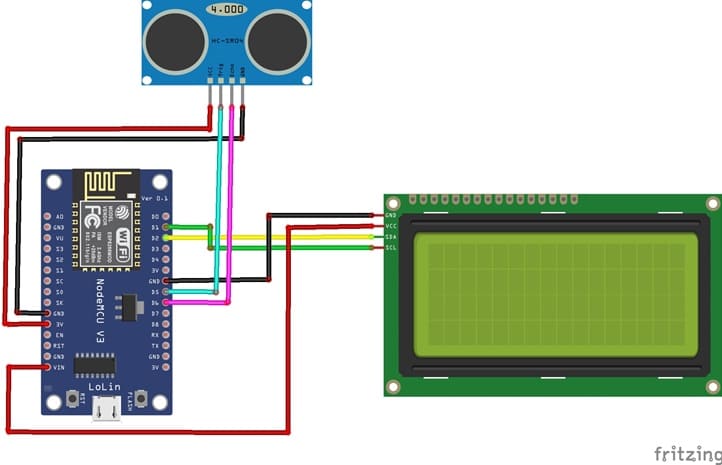
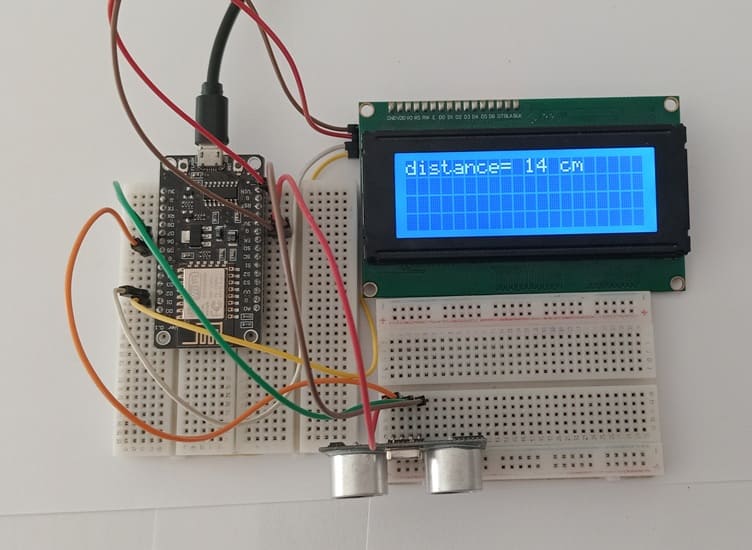
Attaching the I2C LCD Display :
- connect the VCC pin of the display to 5V pin of the ESP8266
- connect the GND pin of the display to GND pin of the ESP8266
- connect the SDA pin of the display to D2 (GPIO4) pin of the ESP8266
- connect the SCL pin of the display to D1 (GPIO5) pin of the ESP8266
Attaching the HC-SR04 sensor :
- Connect the VCC(+) pin of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to the 3.3V pin on the ESP8266 board.
- Connect the Trig pin of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to D5 (GPIO14) pin on the ESP8266 board.
- Connect the Echo pin of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to D6 (GPIO12) pin on the ESP8266 board.
- Connect the GND(-) pin of the HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor to any ground (GND) pin on the ESP8266 board.
Program ESP8266 NodeMCU with MicroPython
To program the ESP8266 board with MicroPython to calculate and display the distance between the HC-SR04 sensor and an object on an I2C LCD screen, you can follow the steps below.
1- import this library : hc-sr04 for HC-SR04 sensor
2- import this two libraries : i2c_lcd and lcd_api for I2C LCD screen
3- Create a new Python script and write the following code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
import machine from machine import Pin, SoftI2C from lcd_api import LcdApi from i2c_lcd import I2cLcd from hcsr04 import HCSR04 import time I2C_ADDR = 0x27 totalRows = 2 totalColumns = 16 # Configure I2C for LCD screen i2c = SoftI2C(scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4), freq=10000) lcd = I2cLcd(i2c, I2C_ADDR, totalRows, totalColumns) # Configure HC-SR04 pins sensor = HCSR04(trigger_pin=14,echo_pin=12,echo_timeout_us=1000000) while True: #calculate distance between the HC-SR04 sensor and an object distance = sensor.distance_cm() print('distance= ',distance,' cm') # show distance on LCD I2C display lcd.putstr("distance= ") lcd.putstr(str(int(distance))) lcd.putstr(" cm") time.sleep_ms(2000) lcd.clear() |
This code continuously measures the distance using the HC-SR04 sensor and displays it on the I2C LCD screen.