Displaying and Scrolling Text on SSD1306 OLED Using ESP8266 NodeMCU
Tutorial plan
1- Objective of the tutorial
2- Introducing the SSD1306 OLED screen
3- The necessary components
4- ESP8266 Assembly with SSD1306 Display
5- Program ESP8266 NodeMCU with MicroPython
Objective of the tutorial
In this tutorial, you will learn how to interface an SSD1306 OLED display with an ESP8266 NodeMCU using MicroPython. The guide will cover how to initialize the OLED display, show static text, and implement scrolling text across the screen.
You will also learn how to use the I2C communication protocol to send data from the ESP8266 to the OLED, as well as how to control the speed and direction of scrolling.
By the end of this tutorial, you will be able to create dynamic text displays suitable for IoT dashboards, notifications, or mini information screens.
This tutorial is ideal for beginners and intermediate makers who want to enhance their ESP8266 projects with an interactive visual display.
Introducing the SSD1306 OLED screen

The SSD1306 OLED is a small, low-power display module widely used in electronics projects. It features organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), which means each pixel emits its own light, eliminating the need for a backlight and allowing for high contrast and wide viewing angles.
Key features of the SSD1306 OLED include:
- resiolution: Typically 128×64 or 128×32 pixels
- interface: Supports I2C and SPI communication, with I2C being the most common for ESP8266 projects
- low Power Consumption: Ideal for battery-powered applications
- compact Size: Small enough to fit on breadboards or embedded devices
The SSD1306 is perfect for displaying text, icons, simple graphics, and animations, making it an excellent choice for IoT projects, status screens, and information displays.
The necessary components
1. ESP8266 NodeMCU Board

It Acts as the main controller, running the MicroPython code and communicating with the OLED display.
2. SSD1306 OLED Display (I2C Interface)

It displays text and graphics. The OLED is very bright, has high contrast, and consumes little power.
3. Jumper Wires

Flexible wires are Used to connect the NodeMCU to the OLED display and optionally to a breadboard.
4. Breadboard

It helps organize connections between the NodeMCU and OLED without soldering, making prototyping easier.
ESP8266 Assembly with SSD1306 Display
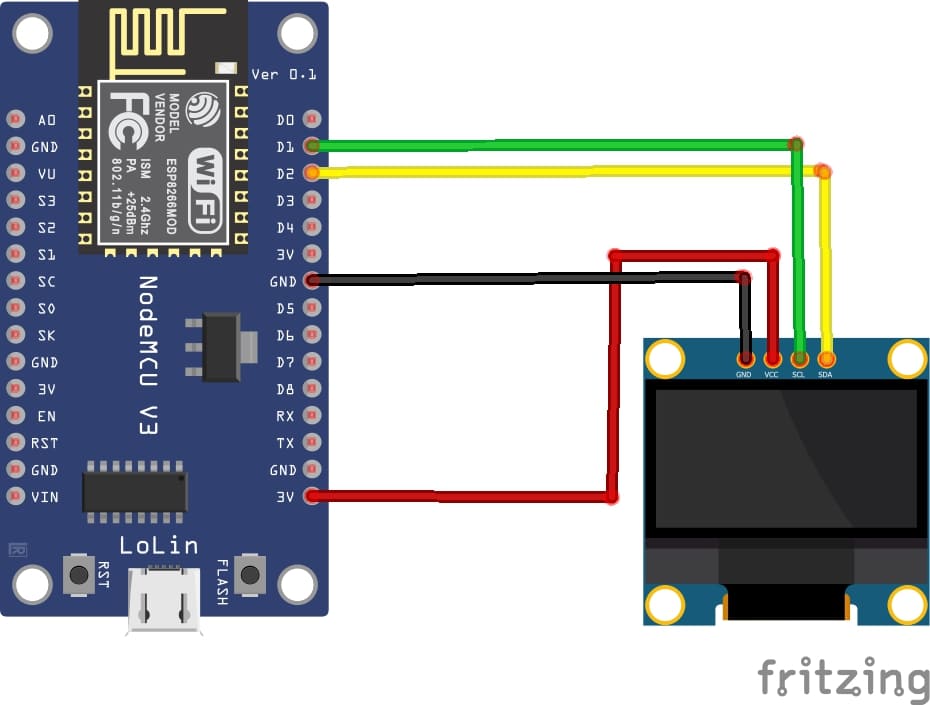
1- Connect the GND pin of the display to the GND pin of the ESP8266 board
2- Connect the VCC pin of the display to the VIN pin of the ESP8266 board
3- Connect the SDA pin of the display to the D2 (GPIO4) pin of the ESP8266 board
4- Connect the SCL pin of the display to the D1 (GPIO5) pin of the ESP8266 board
Program ESP8266 NodeMCU with MicroPython
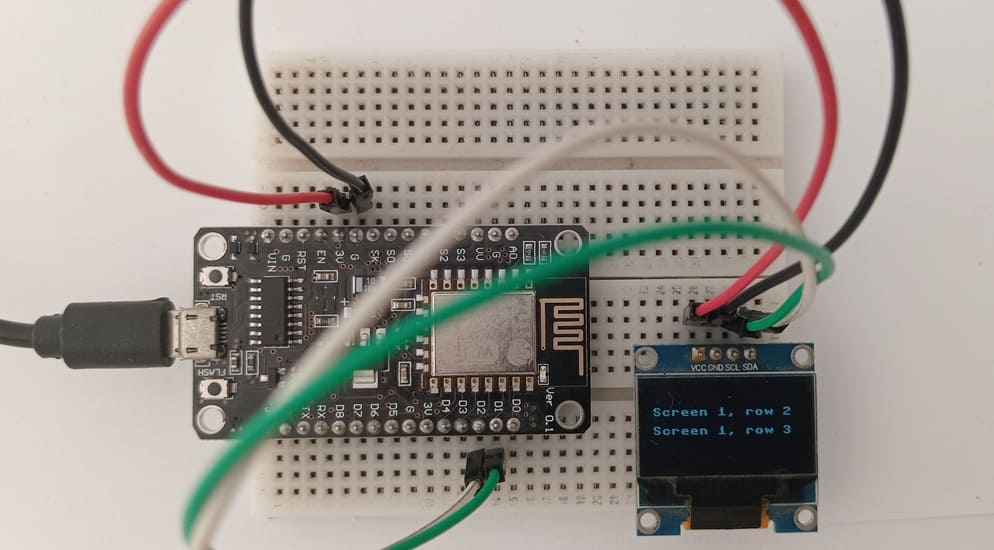
Here is a complete MicroPython program that allows you to scroll text on an SSD1306 screen using the ESP8266 NodeMCU board.
Make sure you have the MicroPython library ssd1306.py installed on your ESP8266.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 |
# Complete project details at https://RandomNerdTutorials.com/micropython-ssd1306-oled-scroll-shapes-esp32-esp8266/ from machine import Pin, SoftI2C import ssd1306 from time import sleep # ESP32 Pin assignment i2c = SoftI2C(scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4)) # ESP8266 Pin assignment #i2c = SoftI2C(scl=Pin(5), sda=Pin(4)) oled_width = 128 oled_height = 64 oled = ssd1306.SSD1306_I2C(oled_width, oled_height, i2c) screen1_row1 = "Screen 1, row 1" screen1_row2 = "Screen 1, row 2" screen1_row3 = "Screen 1, row 3" screen2_row1 = "Screen 2, row 1" screen2_row2 = "Screen 2, row 2" screen3_row1 = "Screen 3, row 1" screen1 = [[0, 0 , screen1_row1], [0, 16, screen1_row2], [0, 32, screen1_row3]] screen2 = [[0, 0 , screen2_row1], [0, 16, screen2_row2]] screen3 = [[0, 40 , screen3_row1]] # Scroll in screen horizontally from left to right def scroll_in_screen(screen): for i in range (0, oled_width+1, 4): for line in screen: oled.text(line[2], -oled_width+i, line[1]) oled.show() if i!= oled_width: oled.fill(0) # Scroll out screen horizontally from left to right def scroll_out_screen(speed): for i in range ((oled_width+1)/speed): for j in range (oled_height): oled.pixel(i, j, 0) oled.scroll(speed,0) oled.show() # Continuous horizontal scroll def scroll_screen_in_out(screen): for i in range (0, (oled_width+1)*2, 1): for line in screen: oled.text(line[2], -oled_width+i, line[1]) oled.show() if i!= oled_width: oled.fill(0) # Scroll in screen vertically def scroll_in_screen_v(screen): for i in range (0, (oled_height+1), 1): for line in screen: oled.text(line[2], line[0], -oled_height+i+line[1]) oled.show() if i!= oled_height: oled.fill(0) # Scroll out screen vertically def scroll_out_screen_v(speed): for i in range ((oled_height+1)/speed): for j in range (oled_width): oled.pixel(j, i, 0) oled.scroll(0,speed) oled.show() # Continous vertical scroll def scroll_screen_in_out_v(screen): for i in range (0, (oled_height*2+1), 1): for line in screen: oled.text(line[2], line[0], -oled_height+i+line[1]) oled.show() if i!= oled_height: oled.fill(0) while True: # Scroll in, stop, scroll out (horizontal) scroll_in_screen(screen1) sleep(2) scroll_out_screen(4) scroll_in_screen(screen2) sleep(2) scroll_out_screen(4) scroll_in_screen(screen3) sleep(2) scroll_out_screen(4) # Continuous horizontal scroll scroll_screen_in_out(screen1) scroll_screen_in_out(screen2) scroll_screen_in_out(screen3) # Scroll in, stop, scroll out (vertical) scroll_in_screen_v(screen1) sleep(2) scroll_out_screen_v(4) scroll_in_screen_v(screen2) sleep(2) scroll_out_screen_v(4) scroll_in_screen_v(screen3) sleep(2) scroll_out_screen_v(4) # Continuous verticall scroll scroll_screen_in_out_v(screen1) scroll_screen_in_out_v(screen2) scroll_screen_in_out_v(screen3) |
The role of this program is to demonstrate how to display and animate text on an SSD1306 OLED using an ESP32 or ESP8266. Specifically, it:
- Displays multiple screens of text – Each “screen” contains one or more lines of text at specified coordinates.
- Scrolls text horizontally and vertically – It shows different animation effects:
- Scroll in (text enters the screen from left or top)
- Scroll out (text exits the screen to right or bottom)
- Continuous scrolling (text moves repeatedly across the screen)
























