Measure weight with HX711 sensor and Arduino UNO
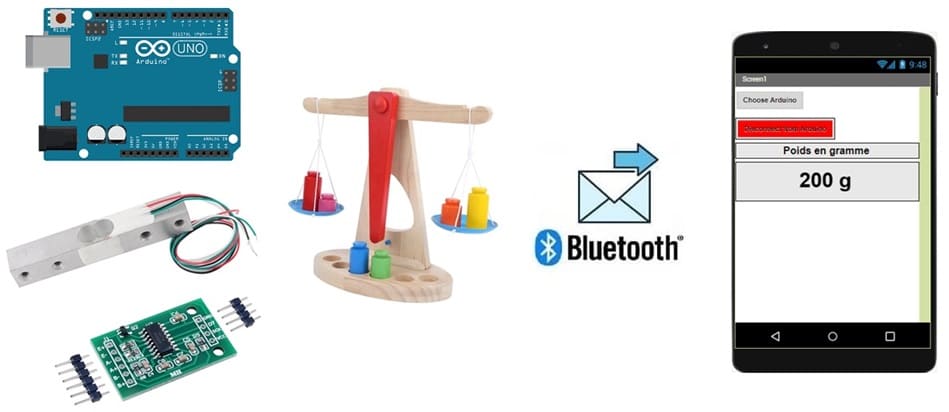

Plan tutorial
1- Presentation of HX711 weight sensor
2- How to send weight measured by HX711 to Samrtphone using Arduino UNO ?
3- Components needed
4- Circuit setup
5- Program Arduino UNO to send weight to Smartphone
6- Develop mobile application with App Inventor to receive weight from Arduino UNO
Presentation of HX711 weight sensor
The HX711 is a precision 24-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) designed for applications requiring accurate weight measurement. It's commonly used with load cells in electronic scales and similar devices.
How It Works
1. Load Cell Connection:
A load cell is a transducer that converts force (weight) into an electrical signal.
The HX711 reads the small voltage changes from the load cell.
2. Signal Amplification:
The module amplifies the low-level signal from the load cell to a readable voltage range.
Channel A has higher precision and is commonly used for weight measurement.
3. Analog-to-Digital Conversion: The amplified signal is converted to a 24-bit digital value for processing.
4. Data Transmission: The HX711 communicates the digital weight data to a microcontroller (e.g., Arduino) via a simple serial protocol.
Applications
Electronic weighing scales.
Force measurement devices.
Industrial automation requiring weight data.
DIY projects like kitchen scales or luggage weighers.
How to send weight measured by HX711 to Samrtphone using Arduino UNO ?
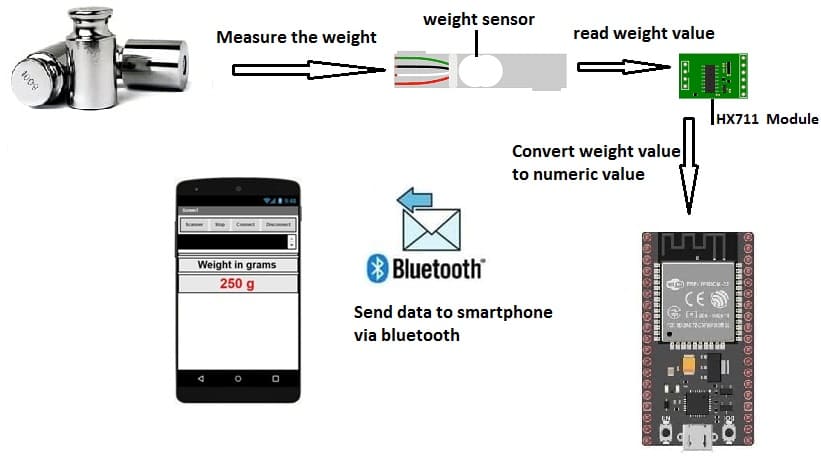
This project involves creating a system to measure weight using the HX711 load cell, transmit the data wirelessly via Bluetooth using an Arduino UNO microcontroller running MicroPython, and display the measured weight on a smartphone app built with MIT App Inventor.
Process Overview
1. Measurement:
The HX711 module reads weight data from the load cell, amplifies the signal, and sends it to the Arduino UNO via digital pins.
2. Data Processing:
Arduino UNO runs MicroPython, reads the weight data from the HX711, and processes it. Arduino UNO uses HC-06 Bluetooth module to transmit the processed data.
3. Bluetooth Communication:
Arduino UNO acts as a Bluetooth server, advertising its availability and sending weight data to any paired device.
4. Smartphone Application:
A custom app built using MIT App Inventor receives the Bluetooth data and displays it in a user-friendly interface.
Components needed
Arduino UNO:
A microcontroller with built-in Bluetooth and Wi-Fi capabilities, acting as the central processor and communication device.
HX711 Module:
A 24-bit ADC (Analog-to-Digital Converter) designed to read the small electrical signals from a load cell.
Load Cell Sensor:

A transducer that converts force (weight) into an electrical signal.
Smartphone:

The display device to receive and show weight data.
Jumper Wires:

For making temporary connections and wiring between components.
Breadboard:

A breadboard is a useful tool for creating temporary electronic circuits. It allows you to connect components without soldering.
Circuit setup
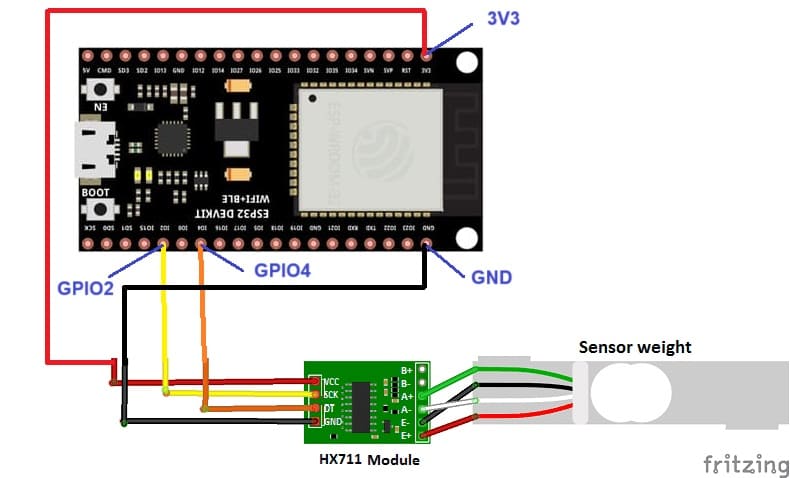
- Connect the VCC pin of the hx711 module to the 3.3V pin of ESP32
- Connect the GND pin of the hx711 module to the GND pin of ESP32
- Connect the DT pin of the hx711 module to the D5 pin of ESP32
- Connect the SCK pin of the hx711 module to the D4 pin of ESP32
- Connect the E+ pin of the hx711 module to the red wire of the weight sensor
- Connect the E- pin of the hx711 module to the black wire of the weight sensor
- Connect pin A- of the hx711 module to the white wire of the weight sensor
- Connect the A+ pin of the hx711 module to the green wire of the weight sensor
Program ESP32 card with Micropython to send weight to Smartphone
To program an ESP32 card using MicroPython to send weight data to a smartphone, you need a few components:
1- Flash your ESP32 with MicroPython using this file esp32-20210902-v1.17.bin.
2- import two libraries : ble_uart_peripheral.py and ble_advertising.pyfor Bluetooth communication.
3- import hx711 library
Here’s a simple code that reads data from the HX711 and sends it to the smartphone via Bluetooth:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 |
from esp_ble_uart import * import time from machine import freq #freq(160000000) from hx711 import HX711 driver = HX711(d_out=5, pd_sck=4) nom = 'ESP32-ble-uart-gcworks' UUID_UART = '6E400001-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E' UUID_TX = '6E400003-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E' UUID_RX = '6E400002-B5A3-F393-E0A9-E50E24DCCA9E' val_rx = "12" uart = Bleuart(nom, UUID_UART, UUID_TX, UUID_RX) uart.close() def rcp_rx(): global val_rx if uart.any(): while uart.any(): val_rx = uart.read().decode().strip() print('sur rx: ', val_rx) def env_tx(val_tx): uart.write(str(val_tx) + '\n') print("tx", val_tx) while True: uart.irq(handler=rcp_rx) print((driver.read()-183200)/238) env_tx(round(((driver.read()-183200)/238)+15)) # the mesured weight sent to smartphone time.sleep_ms(1000) driver.power_off() |
Develop mobile application with App Inventor to receive weight from ESP32
1- Go to MIT App Inventor and create a new project.
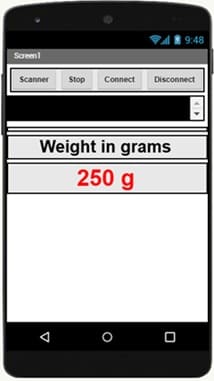
2- Design the User Interface
- Drag and drop components to create the following UI:
- the available Bluetooth components to establish a connection with the ESP32.
- Label: To display the weight.
Here is the Designer part of the application with App Inventor :
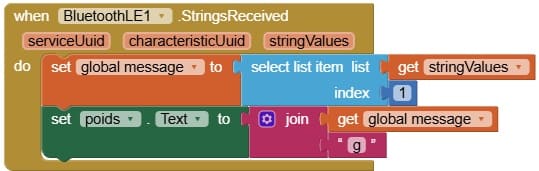
3- Programming the application with App Inventor:
a- Use the available blocks in App Inventor to establish a Bluetooth connection with the ESP32.
- Starting with Android 12, Bluetooth permissions have been enhanced to improve security and user data protection. This is why we must declare the authorizations that your application needs in the AndroidManifest.xml file. For Bluetooth, you'll need to include ACCESS_FINE_LOCATION, BLUETOOTH_SCAN, and possibly BLUETOOTH_CONNECT permissions, depending on the features you're using.
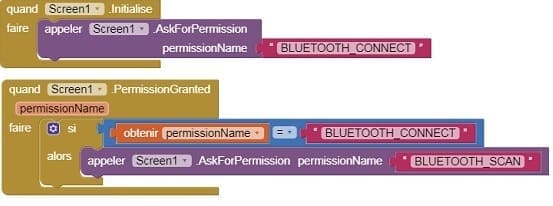
- Use these programming blocks to connect the smartphone to the ESP32 board via Bluetooth:
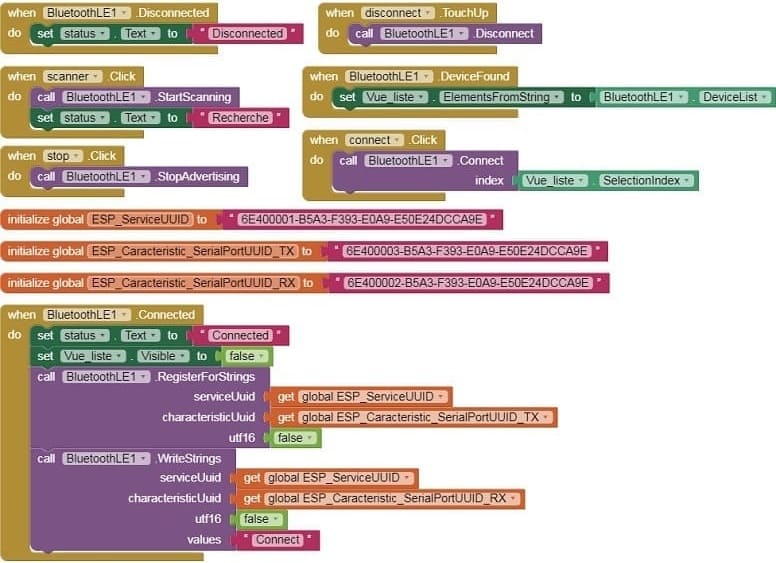
b- Use these programming blocks Receive the weight sent by the ESP32 via Bluetooth and display it in your app.