Micro:bit Line follower robot
Tutorial plan
1- What is line follower robot ?
2- Operation of Micro:bit Line follower robot
3- Robot components
4- Mounting of robot
5- Programming Micro:bit board with Makecode
What is Line follower robot ?
A Line Follower Robot is an autonomous robot designed to follow a pre-defined path, typically a line drawn on a surface. The line is usually black on a white surface or white on a black surface. The robot uses sensors to detect the line and adjusts its movement to stay on the path.
How It Works:
Sensors:
Infrared (IR) sensors or light-dependent resistors (LDRs) are commonly used to detect the contrast between the line and the surface.
Sensors are positioned at the base of the robot to continuously scan the surface.
When a sensor detects the line (high contrast), it signals the controller.
Controller:
A microcontroller (like Arduino, Raspberry Pi, or another embedded system) processes the sensor data and makes decisions.
It calculates how the robot needs to move to stay aligned with the line.
Motors and Actuators:
The robot uses DC motors or servo motors to drive its wheels.
Based on the controller's instructions, the motors adjust the robot's direction.
Algorithm:
A basic algorithm uses conditions like "if left sensor detects the line, turn left; if right sensor detects the line, turn right."
Advanced robots may use PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control to achieve smoother and more accurate line-following.
Operation of Micro:bit Line follower robot
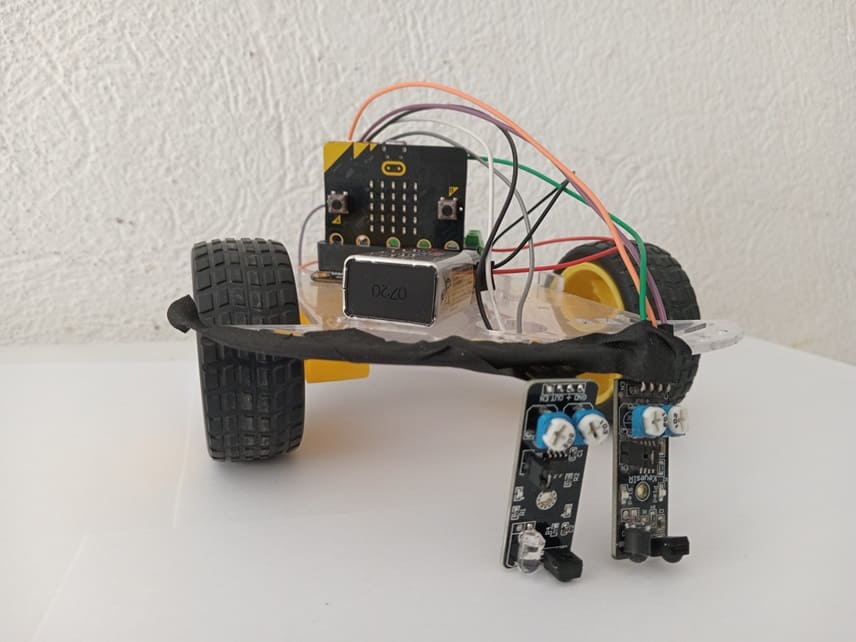
The Micro:bit Line Follower Robot is a two-wheeled robot designed to follow a predefined path, typically a black line on a white surface or vice versa. Using KY-032 infrared (IR) obstacle detection sensors and a Micro:bit Driver Expansion Board, the robot can detect the line's position and adjust its movements to stay on track.
How It Works
Line Detection:
The KY-032 sensors detect the intensity of reflected infrared light.
A black line reflects less IR light than a white surface, which the sensors can distinguish.
Micro:bit Processing:
The Micro:bit reads signals from the sensors.
Based on the sensor readings, the Micro:bit decides whether to move forward, turn left, or turn right to follow the line.
Motor Control:
The Micro:bit sends signals to the driver expansion board to control the motors' speed and direction.
Robot components
Micro:bit microcontroller:
The robot's brain for processing sensor data and controlling movement.
Driver Expansion Board:
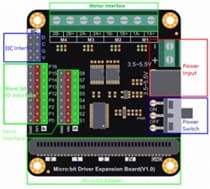
A motor driver compatible with the Micro:bit, often including motor terminals and pin breakouts for sensors.
KY-032 IR Sensors (x2):
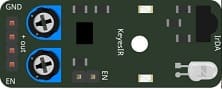
Detect line contrast or obstacles by emitting and detecting infrared light.
Two wheel robot kit

DC Motors with Wheels: Provide movement to the robot.
Chassis: Holds all components together.
Power Source:
Battery pack to power the motors and Micro:bit.
Jumper Wires:

For making temporary connections and wiring between components.
Mounting of robot
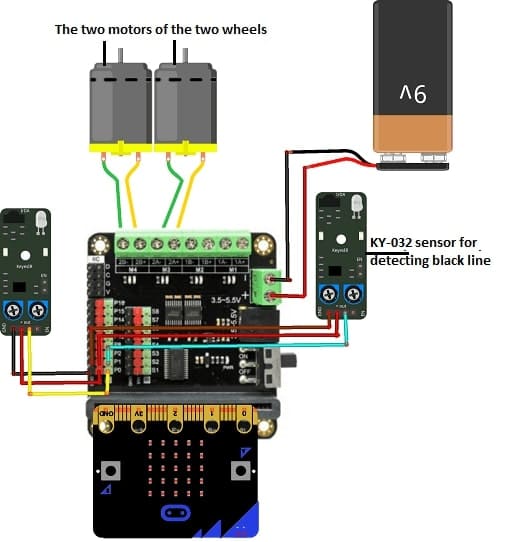
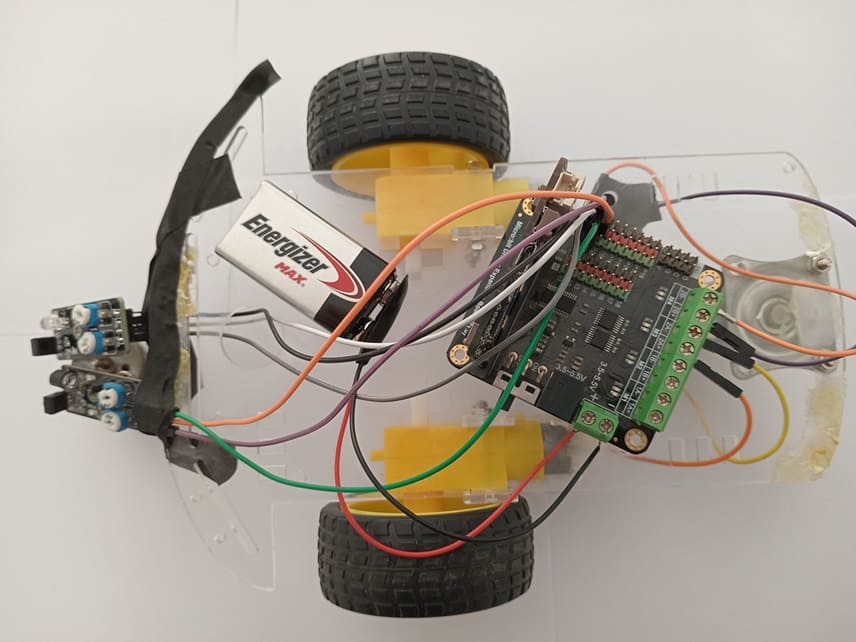
Motor Driver:
Connect the Micro:bit card to the DRIVER EXPANSION board
KY-032 Sensors:
VCC → 3.3V (Micro:bit or driver board)
GND → Ground
OUT → Micro:bit GPIO pins (e.g., P0 for left sensor, P1 for right sensor)
Motor Driver:
VCC and GND → Power source
Motors:
Connect the two motor terminals to the two M3 pins of the DRIVER EXPANSION board
Programming Micro:bit board with Makecode
1- Go to Microsoft MakeCode and start a new project.
2- In MakeCode, open the Blocks Editor (https://makecode.microbit.org/).
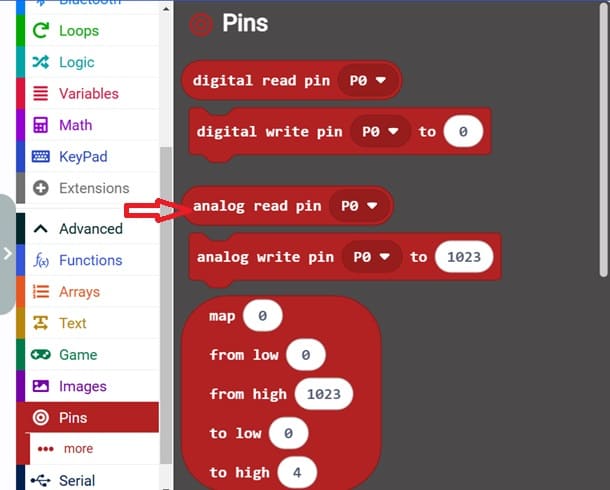
3- Go to Pins and choose 'analog read pin P0' in order to read the value returned by KY-032 sensor.
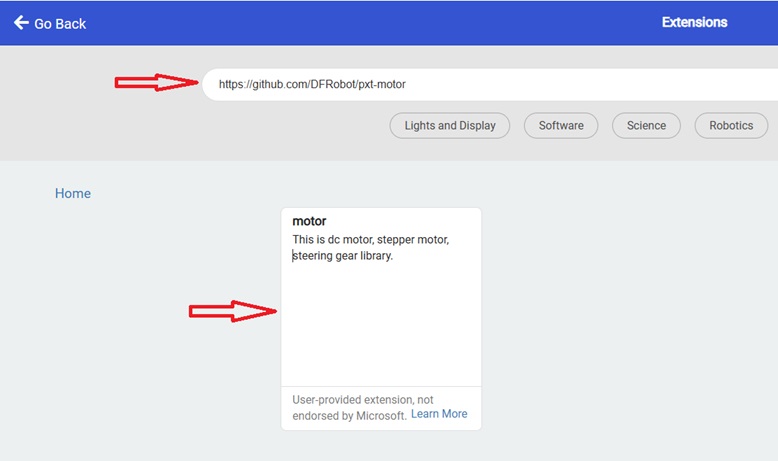
4- Add the Micro:bit Driver Expansion Board extension:
Look for "Extensions" and click on it.

In the search box, insert this link "https://github.com/DFRobot/pxt-motor".
You can now use this blocs to controls the two motors.
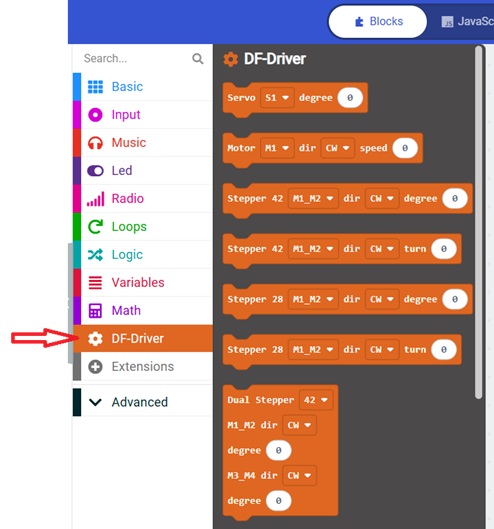
5- Use the blocks provided below to create the program.
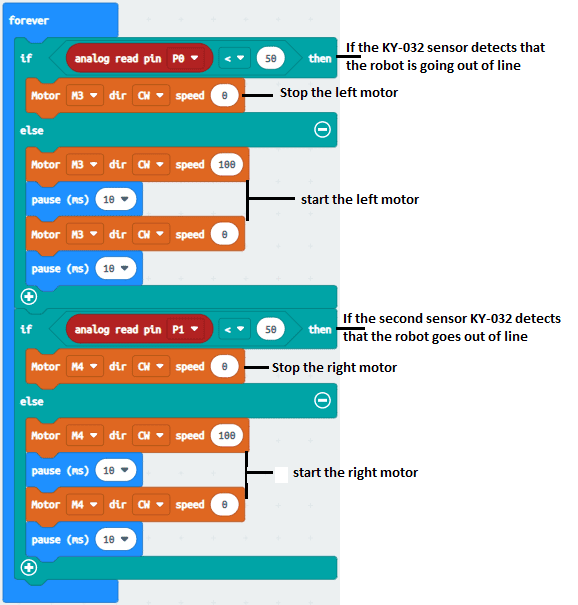
Explanation of Code:
Sensor Logic:
The KY-032 sensors output 0 on detecting a black line and 1 for white areas.
The Micro:bit reads these signals to determine which way to steer the robot.
Motor Control:
The motor function adjusts motor speed to steer the robot.
Depending on sensor input, the robot adjusts its left or right motor speeds.
Testing and Calibration:
1- Place the robot on a test track with a black line on a white background.
2- Test and adjust the motor speeds in the code to ensure smooth turning and line-following behavior.
3- Adjust the sensitivity of the KY-032 sensors using the onboard potentiometer.